Rail-Structure Interaction
Overview
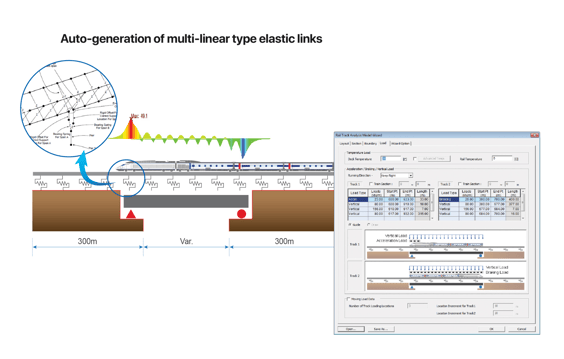
Step 1
+ Rail track analysis model wizard
+ Static loads & Link boundaries
+ Train load generator
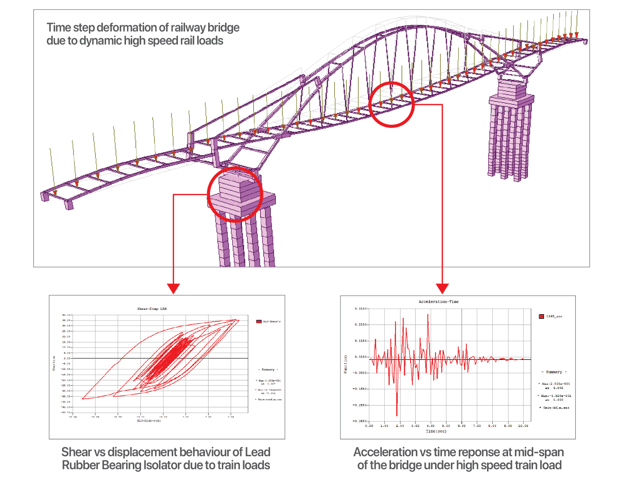
Step 2
+ Static analysis
+ Time history analysis
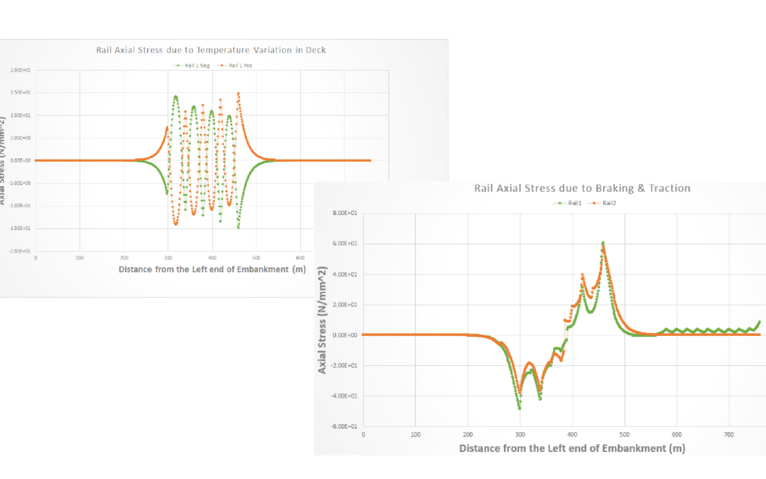
Step 3
+ Rail track analysis report
+ Time history results/graph
In midas Civil, two methods of rail-structure interaction analysis are proposed. The first one is a static analysis and the other is a time history analysis that checks dynamic responses. In static analysis, the user can check the results after manual modeling. In particular, Rail Track Analysis Model & Report Wizard are provided to solve the hard work and inaccuracies of modeling continuously welded rails. Furthermore, they provide descriptions and functions of load and boundary conditions for RSI analysis.
Details
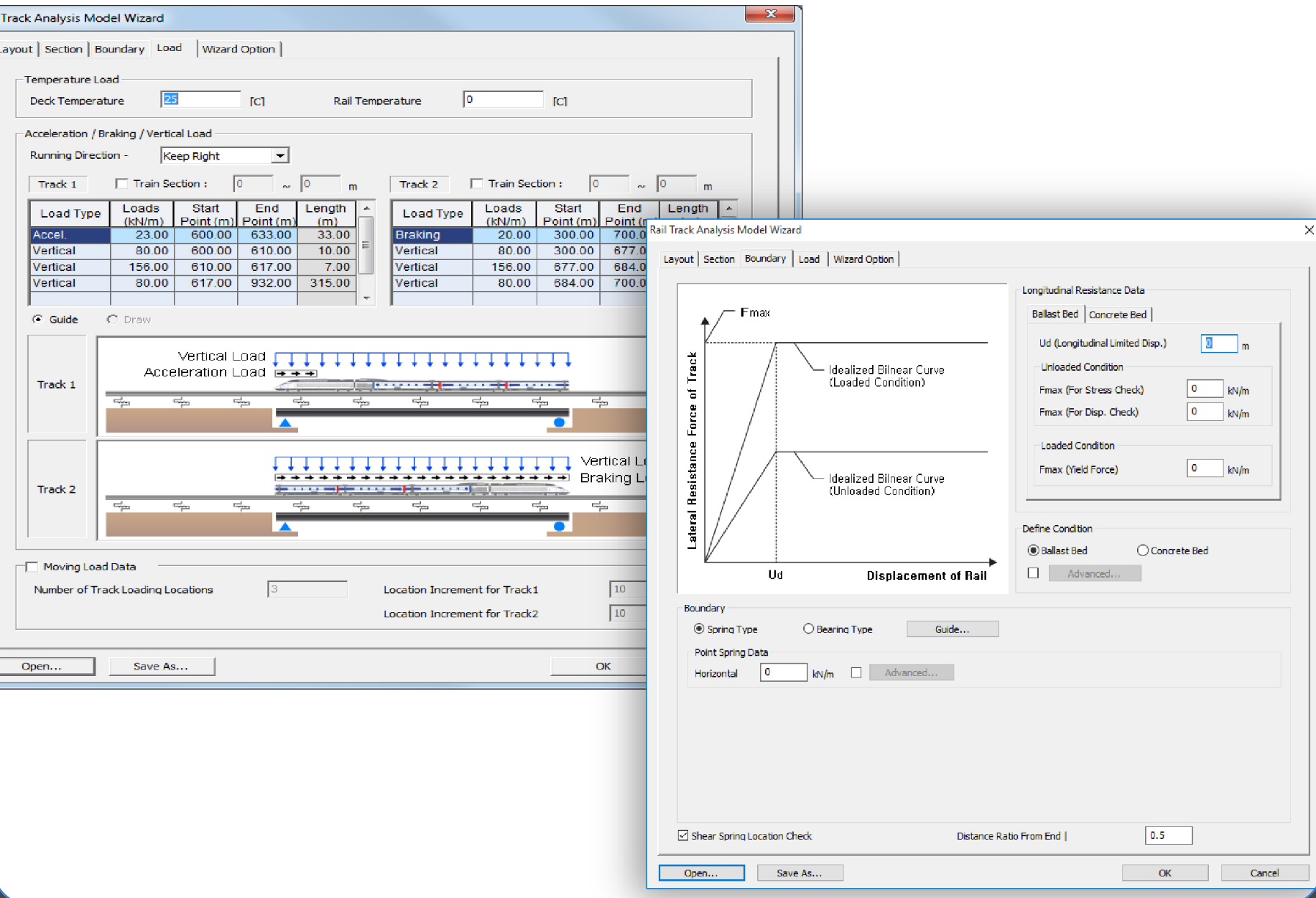
Rail Track Analysis Model Wizard
Rail Track Analysis Model Wizard receives simple input values for rail, bridge structure, and embankment models, and automatically creates an analytical model that includes sections, boundary conditions, and loads. The wizard provides three modeling options:
- Automatic modeling for simplified separate analysis
- Automatic modeling for moving load analysis
- Automatic modeling for stage analysis
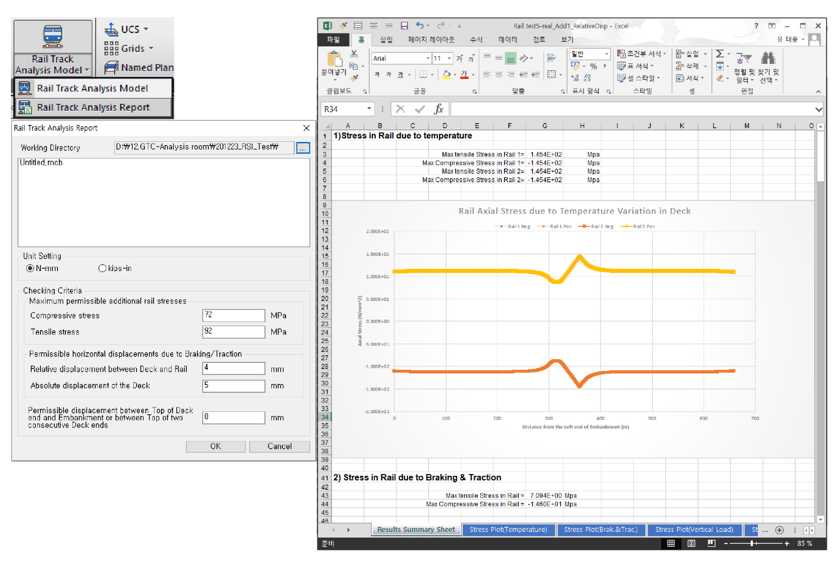
Rail Track Analysis Report Wizard
As a post-processing feature, Rail Track Analysis Report Wizard can be used to analyze all models and obtain compiled excel files. It provides a final summary sheet with checks based on UIC 774-3. These check limits are manually modified for regional codes. The report will contain tabulated data as well as graphical outputs for individual rail stresses, rail and deck relative displacements, and deck absolute displacements.
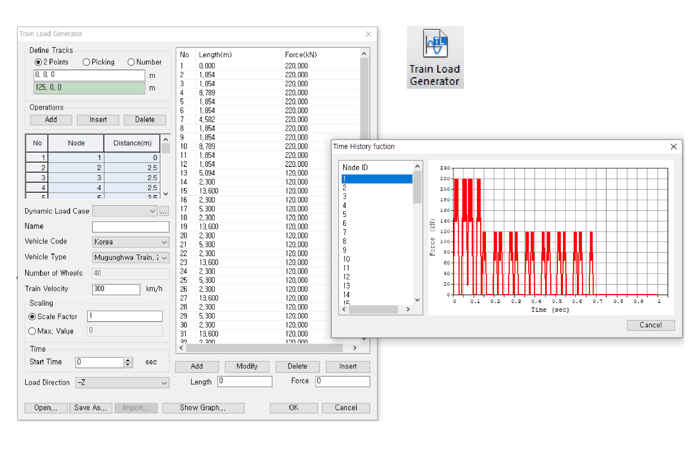
Train Load Generator
Generate time-forcing functions without considering the length of the element along the track. The required nodal spacing along the track is automatically detected by the program. The train load generator function also creates a time-force curve for train loads. Furthermore, the dynamic nodal load for time history analysis is automatically inputted using the time-force curve created in the node located in the designated track.