Moving Load Analysis
Overview
Step 1
+ Traffic line lanes
+ Traffic surface lanes
+ Moving load optimization
Step 2
+ Vehicles
+ Moving load cases
Step 3
+ Influence line/Surface
+ Moving load tracer
The moving load analysis function in midas Civil is used to statically analyze and design bridge structures for vehicle moving loads. Important features are included as follows:
Generation of influence line and influence surface for displacements, member forces, and reactions due to moving loads. Calculation of maximum/minimum nodal displacements, member forces, and support reactions for a given moving vehicle load using generated influence line and influence surface.
Details
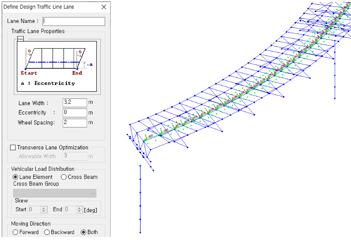
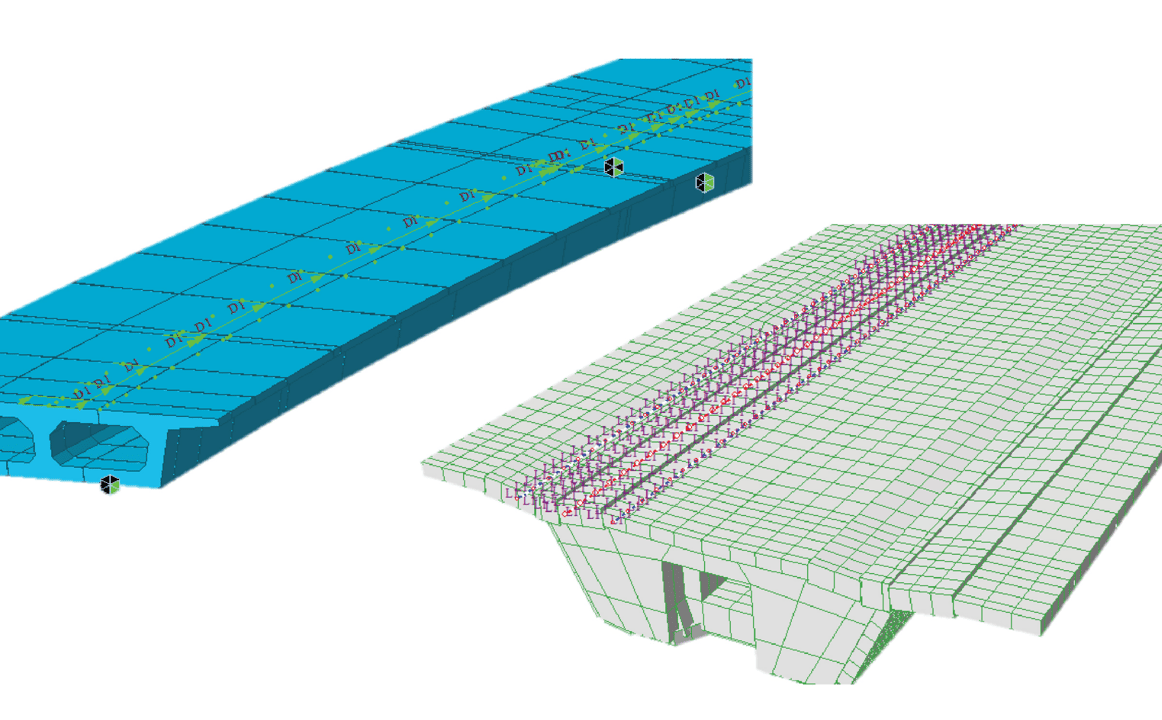
Traffic Line/Surface Lanes
The moving load analysis in midas Civil is effectively performed based on the influence line/surface analysis. To do this, create a traffic line lane or traffic surface lane. It is possible to define traffic lanes for various shapes of elements. Furthermore, by providing options to respond to country-specific design standards and structure types, it is possible to define traffic lanes according to the intention of the engineer. In particular, the optimization function allows the program to automatically consider the location of more moving loads without defining additional traffic lanes.
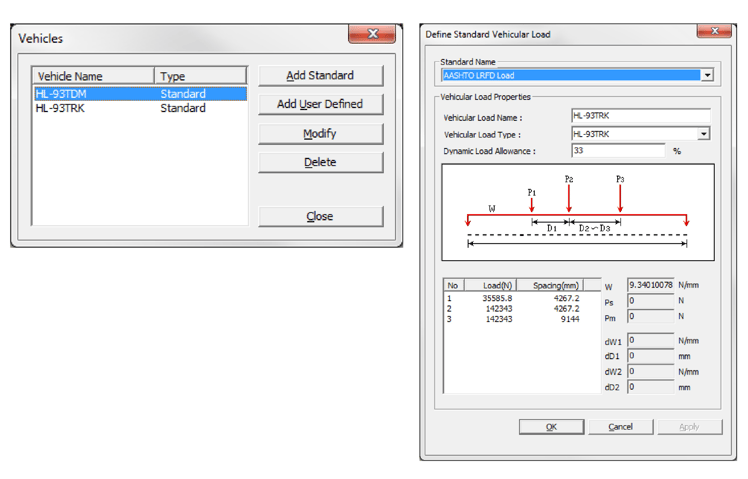
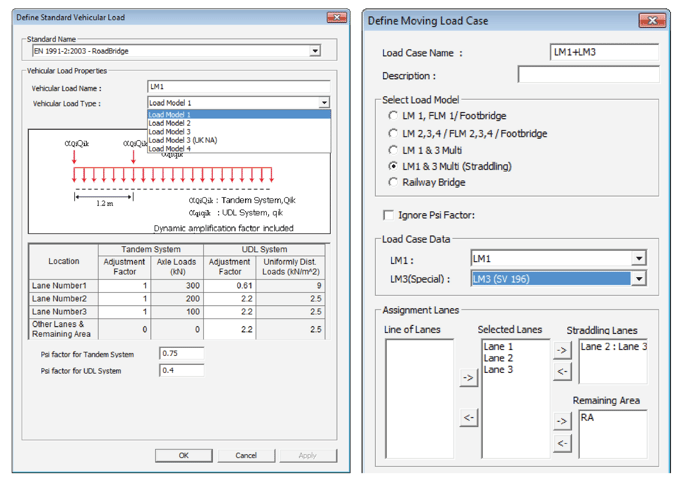
Vehicles & Moving Load Cases
midas Civil provides vehicle load models for each country-specific design code. Furthermore, user-defined functions are also provided to cope with various design environments. In the moving load case function, the user can define moving load cases that meet the country’s design standards by combining traffic lanes and vehicles.
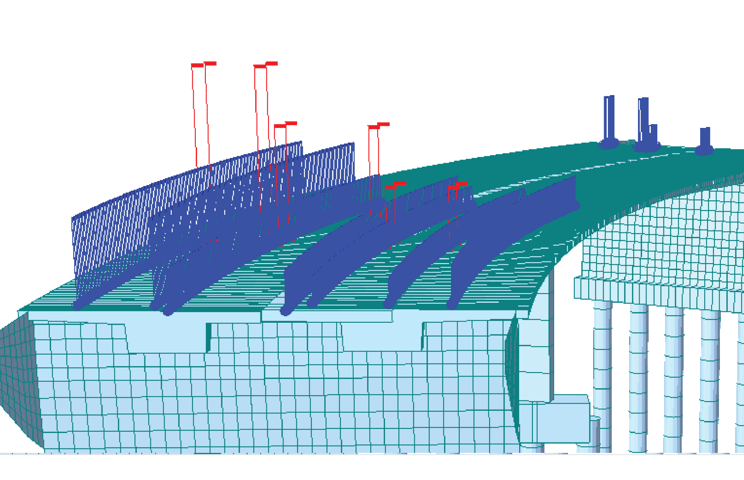
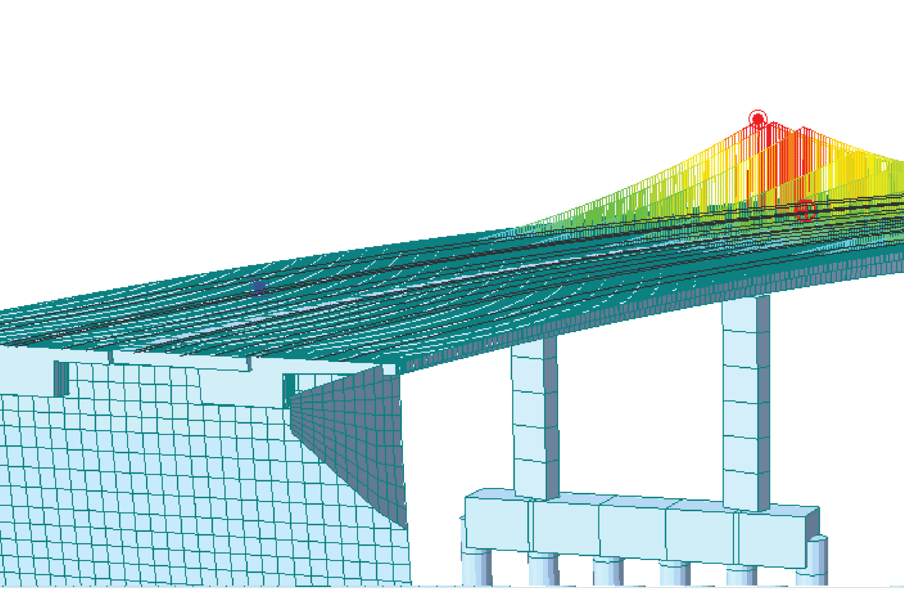
Moving Load Tracer
When moving load analysis is completed, the user can check the envelop results of the analysis, such as the maximum/minimum member force/displacement. The moving load tracer function shows the distribution of the vehicle moving load that represents critical results of the analysis with influence line/surface diagrams. Furthermore, this function selects a specific moving load and converts it to a static load so that it can be used as a load for further analysis.