Dynamic Analysis
Overview
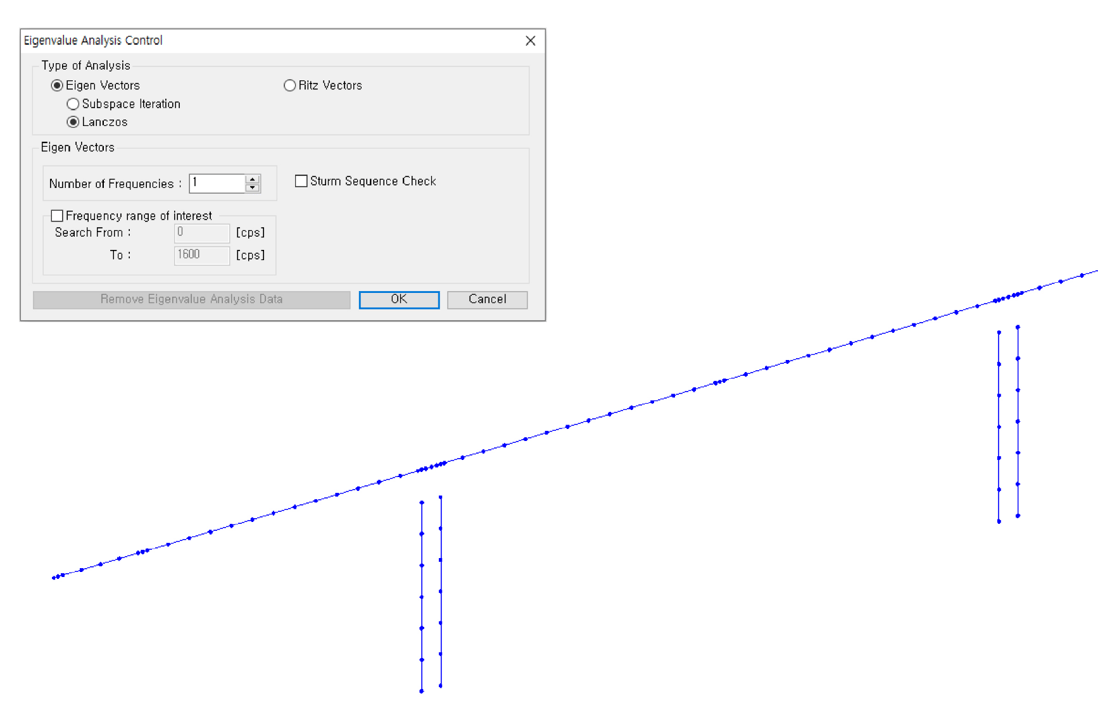
Step 1
+ Eigenvalue analysis control
+ Nodal masses/Loads to masses
+ Rail track interaction analysis wizard
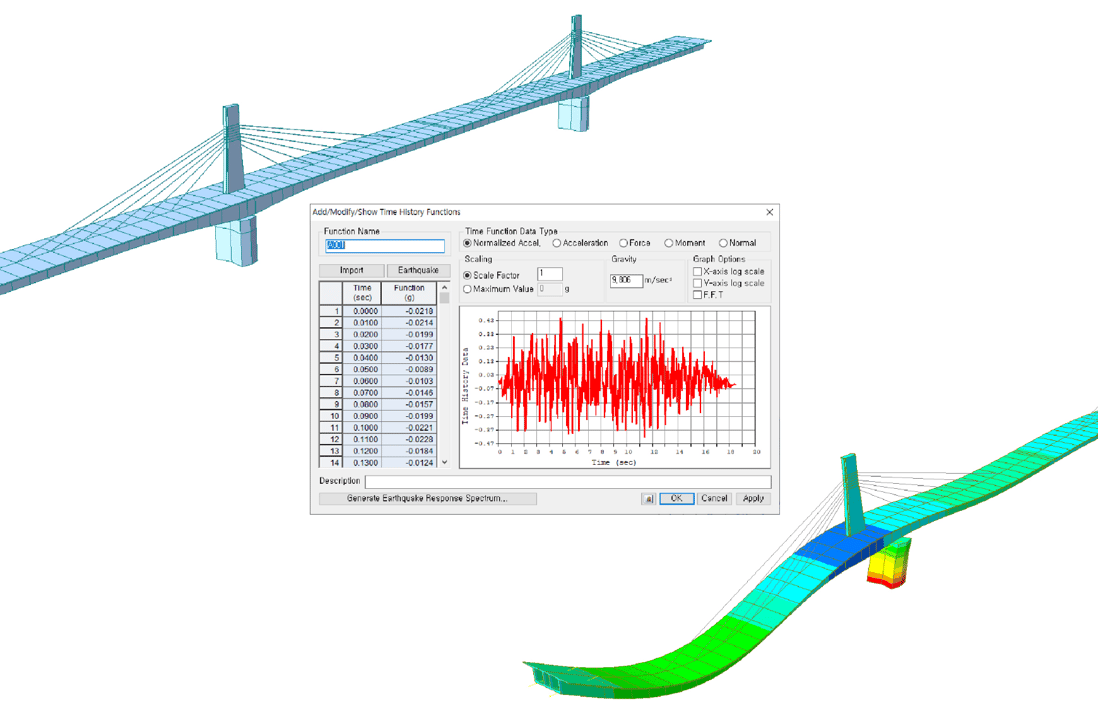
Step 2
+ Response spectrum analysis
+ Time history analysis
+ Dynamic analysis for railway bridge
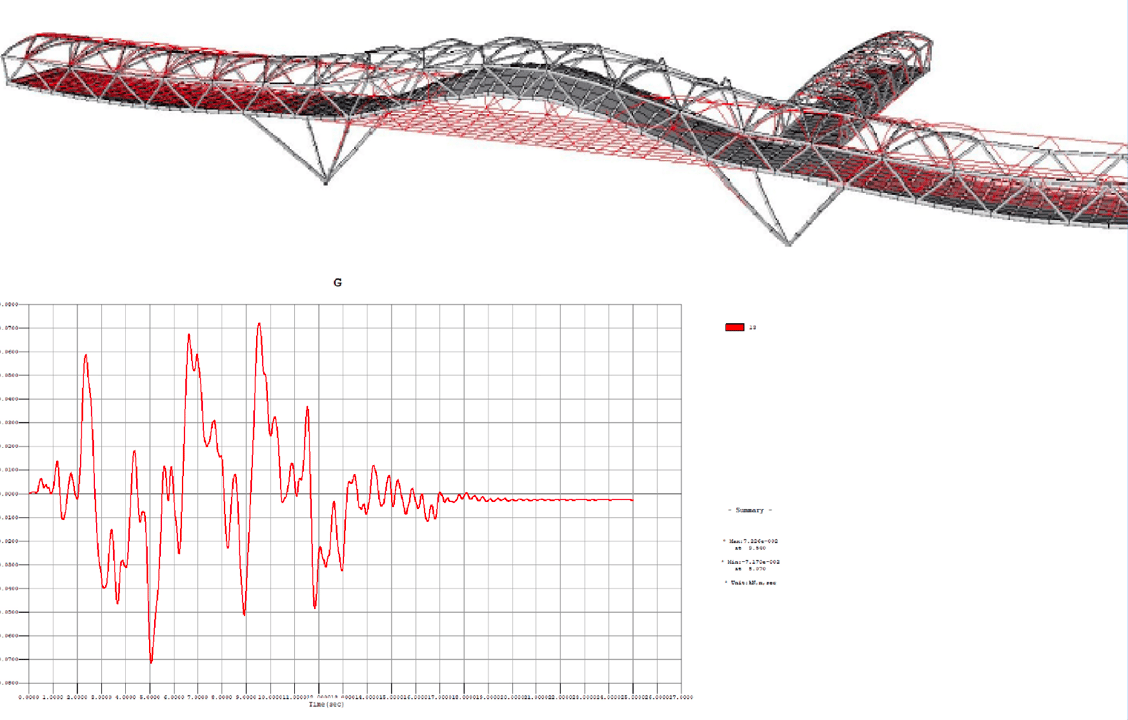
Step 3
+ Mode shapes/Modal damping ratio
+ Time history results
Through midas Civil, the user can perform dynamic analysis of structures such as seismic design, rail-structure interaction, and dynamic behavior of pedestrian bridges. In order to perform dynamic analysis, midas Civil provides eigenvalue analysis, response spectrum analysis, and time history analysis. Furthermore, midas Civil’s Boundary Change Assignment function enables static analysis and dynamic analysis in one model file.
Details
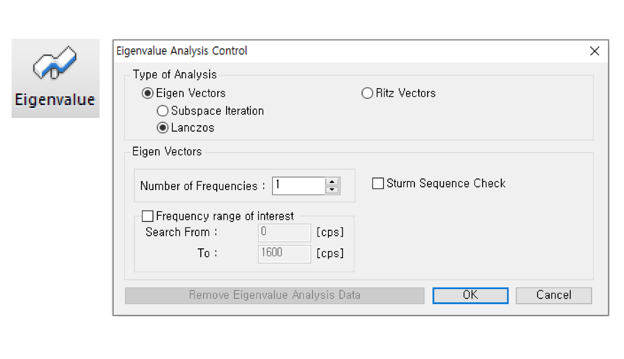
Eigenvalue Analysis Control
In midas Civil, the user can consider time-dependent characteristics of concrete such as Creep, Shrinkage, and Aging. Furthermore, the user can also consider the time-dependent characteristics of steel such as relaxation. All time-dependent characteristics are based on the design code, and user-defined options are also provided to consider various design conditions.
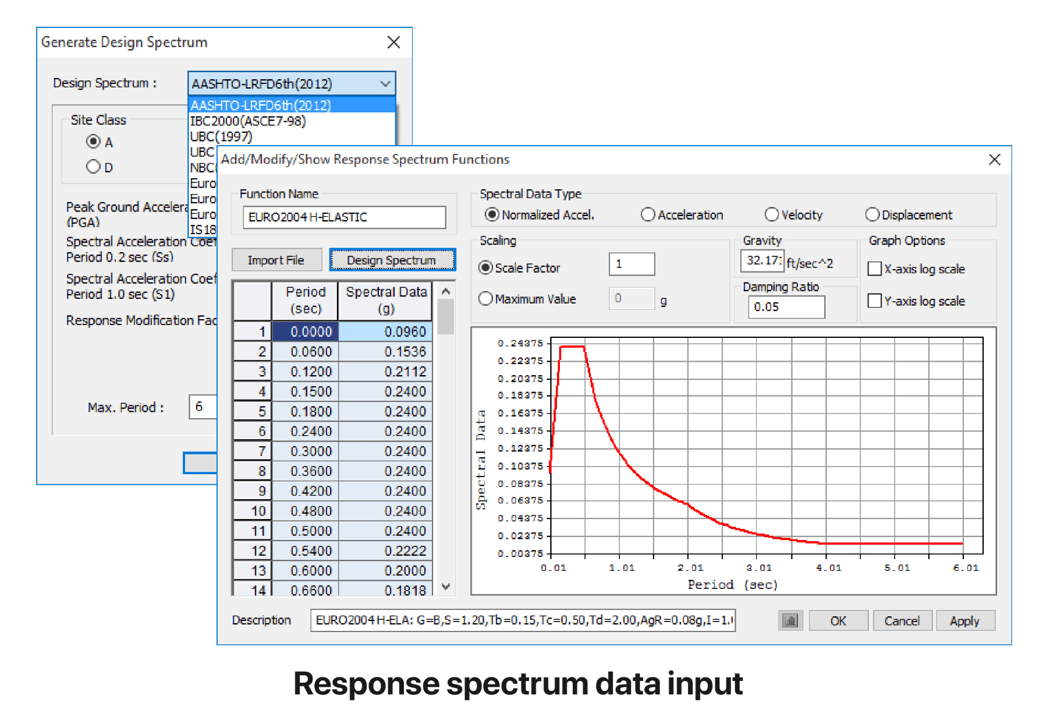
Response Spectrum Functions & Load Cases
In midas Civil, it is possible to analyze the response spectrum for the Z direction and the X-Y plane direction of the global coordinate system. For the modal combination, the user can use the Complete Quadratic Combination (CQC) method and the Square Root of the Sum of the Squares (SRSS) method depending on the user’s choice. Design spectrum and earthquake data for seismic design are provided by region and design codes.
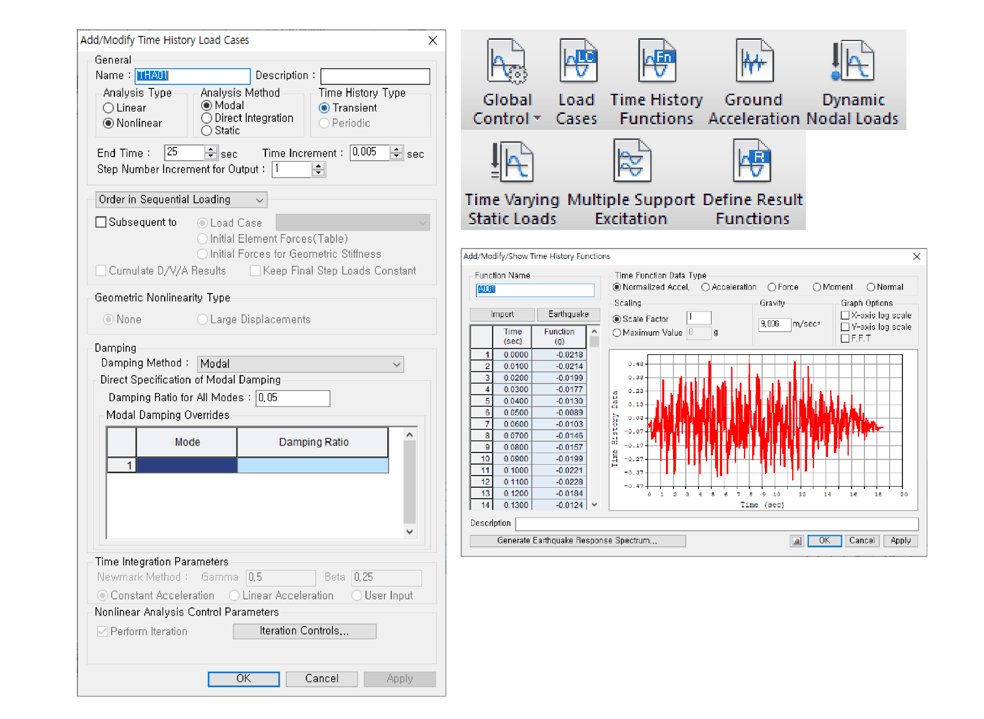
Time History Load Cases & Time Forcing Functions
midas Civil provides a modal superposition method and direct integration for time history analysis. The Time forcing function allows users to consider dynamic loads such as ground acceleration, dynamic nodal loads, and time-varying static loads in order to perform various different analyses. Furthermore, it also allows users to consider time-variable static loads for various analyses.