
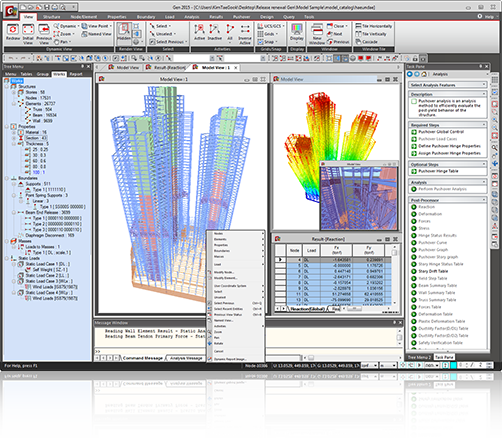
midas Gen
|
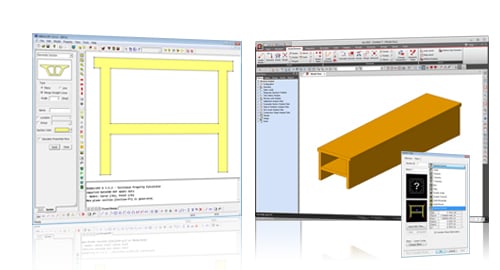
midas Gen provides SPC, which calculates stiffness data for any shape or form. The section shape can be drawn, or a DXF file can be imported. The shape and properties of the generated section can be exported to midas Gen. |
 |
|
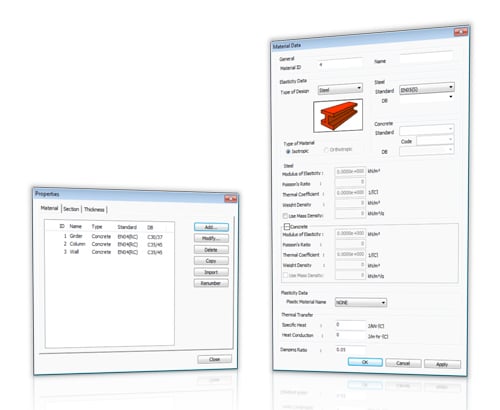
midas Gen contains the material and section database of ASTM, AISC, CISC, CSA, BS, DIN, EN, UNI, IS, JIS, GB, etc. User-defined material and section data can be also implemented. |
 |
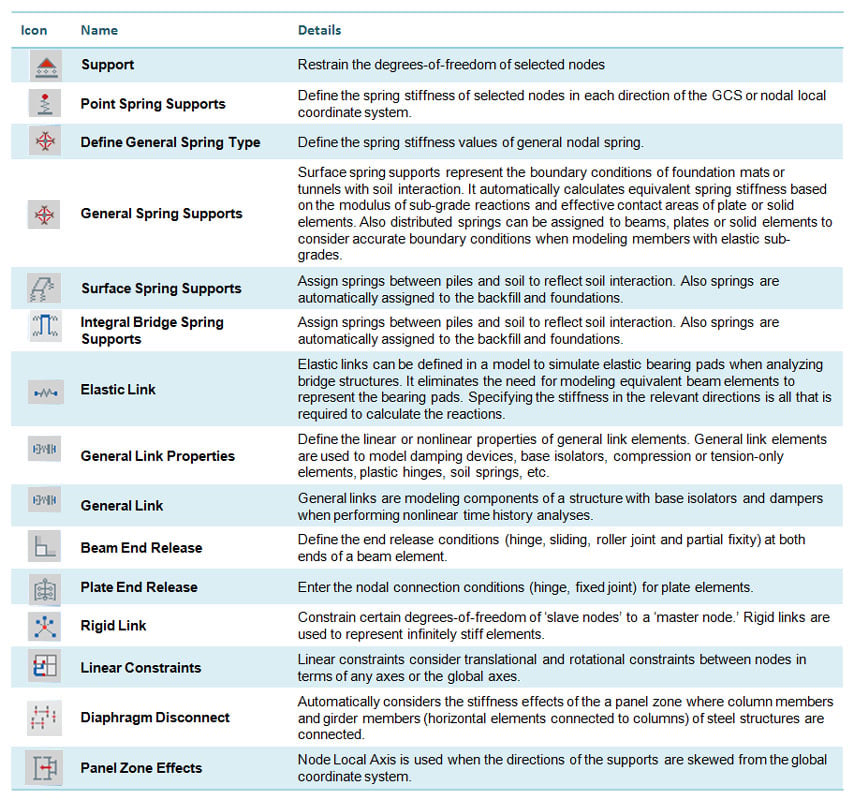
Boundary conditions that midas Gen provides include General Spring Supports designed to incorporate lateral stiffness of piles,
Compression-only boundary elements capable of representing foundations and Tension-only boundary elements.
|
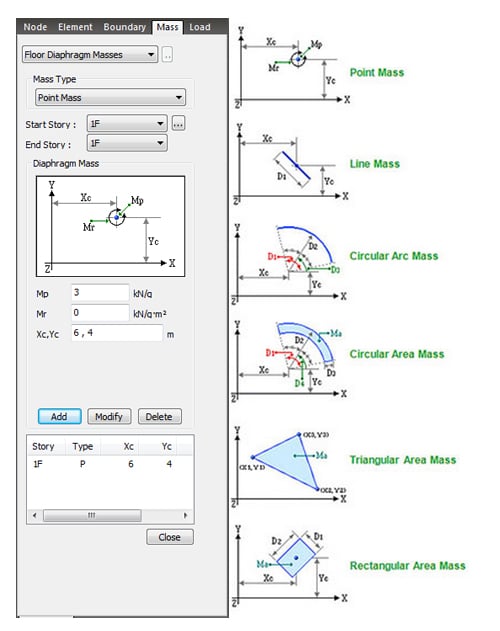
Nodal Masses Lumped Translational Mass/Rotational Mass Moment of Inertia Floor Diaphragm Masses Methods of specifying floor mass data Loads to Masses Vertical components (loads acting in the -Z direction of GCS) of the entered loads are converted into masses, which are entered as concentrated mass data. Consistent Mass Convert into distributed masses. Consistent Mass is calculated with the shape function used to derive the stiffness matrix. Off-diagonal mass terms are considered and, unlike the lumped mass, the inertia coupling effect is considered. Therefore, results using the consistent Self-weight to Mass The masses of the elements included in the model can be automatically converted into lumped masses or consistent masses in midas Gen for dynamic analysis or computation of statically equivalent seismic loads. |
 |
|
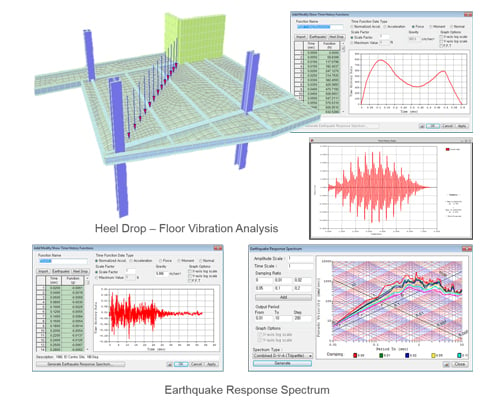
Serviceability of a floor structure can be evaluated by time history analyses. midas Gen provides a number of time history forcing functions for walking loads for floor vibrations IBC2000, UBC, NBC, Eurocode-8, China, IS1893, Taiwan, Japan, Korea. The self-weight of a structure and its loadings can be auto-converted into masses for an eigenvalue analysis. By performing response spectrum analysis, excitation angle of response spectrum is automatically taken as the major-axis direction of a building. |
 |
|
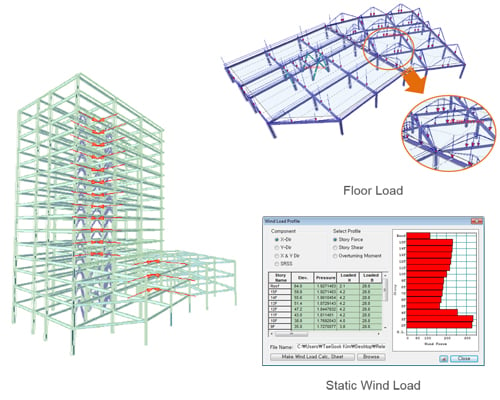
midas Gen provides complete load types. |
 |